Google’s Strategic Play in the AR Glasses Market
Google is making bold moves in the extended reality (XR) space. According to Bloomberg, the tech giant is finalizing a deal to acquire AdHawk Microsystems, an innovative eye-tracking startup, for $100 million, with an additional $15 million in performance-based incentives, bringing the total deal value to $115 million.
Once completed, AdHawk’s team will be integrated into Google’s Android XR division, marking one of Google’s biggest XR-related acquisitions in the last five years. But why is Google so eager to secure this startup?
AdHawk’s Eye-Tracking Tech: A Game-Changer for AR Glasses?
Traditional Eye-Tracking vs. AdHawk’s MEMS Micro-Mirror Solution
Most VR headsets and AR glasses today rely on infrared cameras and LED light sources for eye-tracking. Infrared LEDs illuminate the eye, and cameras capture reflections to determine gaze direction.
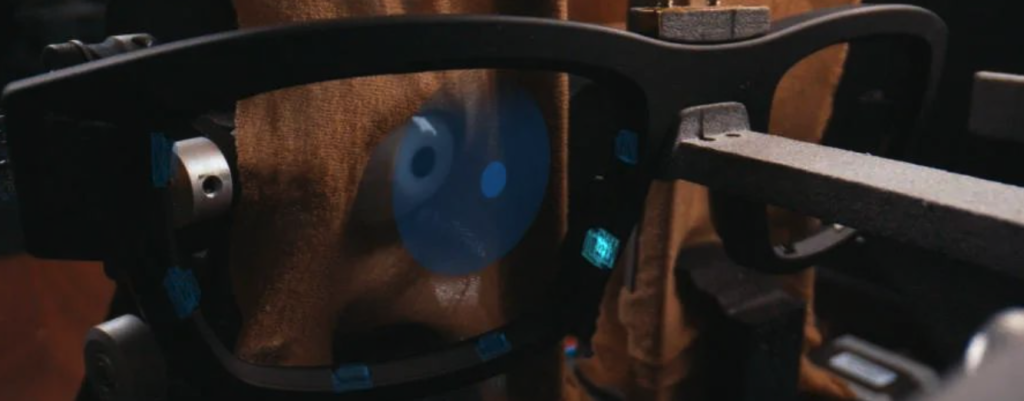
AdHawk is disrupting this approach with MEMS micro-mirror technology.
What is MEMS Micro-Mirror Eye-Tracking?
- MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) micro-mirrors are tiny, chip-scale mirrors that direct light beams with extreme precision.
- Instead of using infrared cameras, AdHawk’s technology uses MEMS micro-mirrors to scan the eye thousands of times per second, capturing high-speed, low-latency eye movement data.
Why MEMS Eye-Tracking Is Perfect for AI-Powered AR Glasses
Compared to traditional camera-based eye-tracking, AdHawk’s MEMS solution offers:
- Miniaturization: MEMS mirrors are chip-scale, making them ideal for compact AR glasses and AI wearables.
- Lower Power Consumption: Unlike camera-based eye-tracking, which consumes significant power, MEMS mirrors require minimal energy, allowing for longer battery life.
- High-Speed, Low-Latency Tracking: MEMS-based scanning achieves 4ms latency and refresh rates of up to 500Hz, outperforming traditional systems.
- Reduced Data Load: MEMS-generated data is 1,000 times smaller than that of camera-based solutions, making it easier to process in real time.

These advantages make AdHawk’s technology a perfect fit for next-gen AI glasses, AR headsets, and lightweight XR devices, where efficiency, battery life, and real-time interaction are critical.
Why Did Google Acquire AdHawk? A Look at the Bigger Picture
Google’s acquisition of AdHawk Microsystems isn’t just about new hardware—it’s a strategic move to strengthen the Android XR ecosystem and compete with Apple Vision Pro and Meta’s Quest devices.
Who Is AdHawk? The Startup That Caught Google’s Eye
Founded in 2015 in Waterloo, Canada, AdHawk Microsystems has been a leader in MEMS eye-tracking technology, attracting interest from major players like Apple, Meta, Sony, and Samsung.
AdHawk’s Funding History & Key Investors:
- 2017 – Raised $4.6M (led by Intel)
- 2019 – Raised $9M (Samsung Ventures)
- 2020 – Raised $3.2M (Silicon Valley Bank)
- 2025 – Acquired by Google for $115M
AdHawk’s technology was previously explored by Meta, Apple, and Sony, but Google ultimately closed the deal.
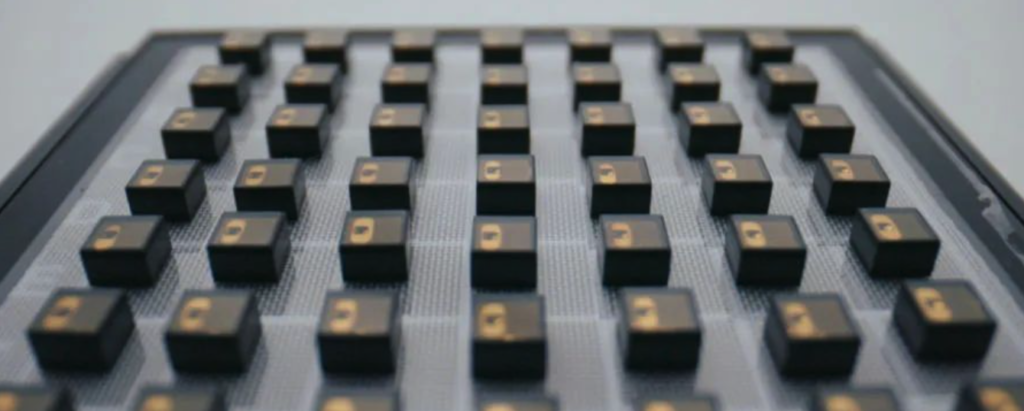
AdHawk’s Eye-Tracking Tech: More Than Just a Sensor
Beyond its core MEMS scanning module, AdHawk has developed full-fledged eye-tracking solutions, including:
- AdHawk MindLink Glasses ($10,000) – High-precision real-time eye-tracking for medical, research, and AR/VR applications.
- AdHawk MindLink Air – Lightweight AI-powered fitness tracking glasses with 12+ hours of battery life.
- AdHawk Eye Robot – A robotic eye module used for VR eye-tracking system validation.
- AdHawk Eyebox Software – Advanced simulation and real-time eye-tracking data analysis tools.

AdHawk’s portfolio makes it clear: Google isn’t just buying hardware—they’re acquiring cutting-edge eye-tracking AI and software, positioning themselves as a major player in next-gen human-computer interaction.

Google’s Grand Plan for Android XR—What’s Next?
With Apple Vision Pro leading the premium XR market and Meta’s Quest and Ray-Ban smart glasses dominating consumer AR, Google needs a breakthrough strategy. AdHawk’s MEMS eye-tracking could be the missing piece in that puzzle.

Key Strategic Benefits of Google’s Acquisition:
- Competing with Apple Vision Pro – AdHawk’s low-power, high-precision tracking could help Google deliver an AI-driven AR experience at a fraction of the cost.
- Strengthening Android XR – Google’s ARCore and Samsung collaboration (Project Mooha) could integrate AdHawk’s eye-tracking for a unified Android XR ecosystem.
- Boosting AI-Powered Interaction – With faster, real-time eye-tracking, Google can enhance AI-based UI navigation, AR gaming, and metaverse applications.
How This Impacts the Global XR Market
Google’s AdHawk acquisition could have ripple effects across the AR and AI glasses industry, particularly for Chinese manufacturers like Thunderbolt, XREAL, and Rokid.
If Google integrates MEMS eye-tracking as a system-level Android API, it could:
✅ Lower Costs & Standardize Eye-Tracking – Making it more accessible to AR/VR manufacturers worldwide.
✅ Enhance AI & Ad Revenue – Eye-tracking data could power AI-driven ads, gaze-based UI, and real-time interaction models.
✅ Accelerate the AI Glasses Revolution – With better battery life, performance, and real-time tracking, Google’s AR push could rival Apple’s ecosystem.
Final Thoughts: Google’s Big Bet on Eye-Tracking & AI Glasses
Google’s $115M acquisition of AdHawk Microsystems signals its ambition to dominate the next wave of AI-powered AR glasses.
With MEMS eye-tracking, Google is setting the stage for longer battery life, ultra-fast gaze control, and seamless AI-driven AR experiences—something Apple, Meta, and Samsung will be watching closely.
Will this boost Android XR adoption in 2025? Only time will tell. But one thing is clear: the race for AI-powered smart glasses is heating up, and Google just made a game-changing move.



now what